
Global Automotive Market in June 2024: China Maintains Lead, Sales Fall in 11 Countries
According to relevant data, global light vehicle sales in June 2024 are estimated to be around 7.6 million units, a year-on-year decrease of 2.2%, though cumulative sales for the first six months still increased by 2.3% year-on-year. For the month, the annual sales rate of global light vehicles reached 89 million units, not only an improvement from May but also the best performance so far this year.
Global Automotive Market Overview: Decline in China and U.S. Sales, Europe Grows by 3.6%
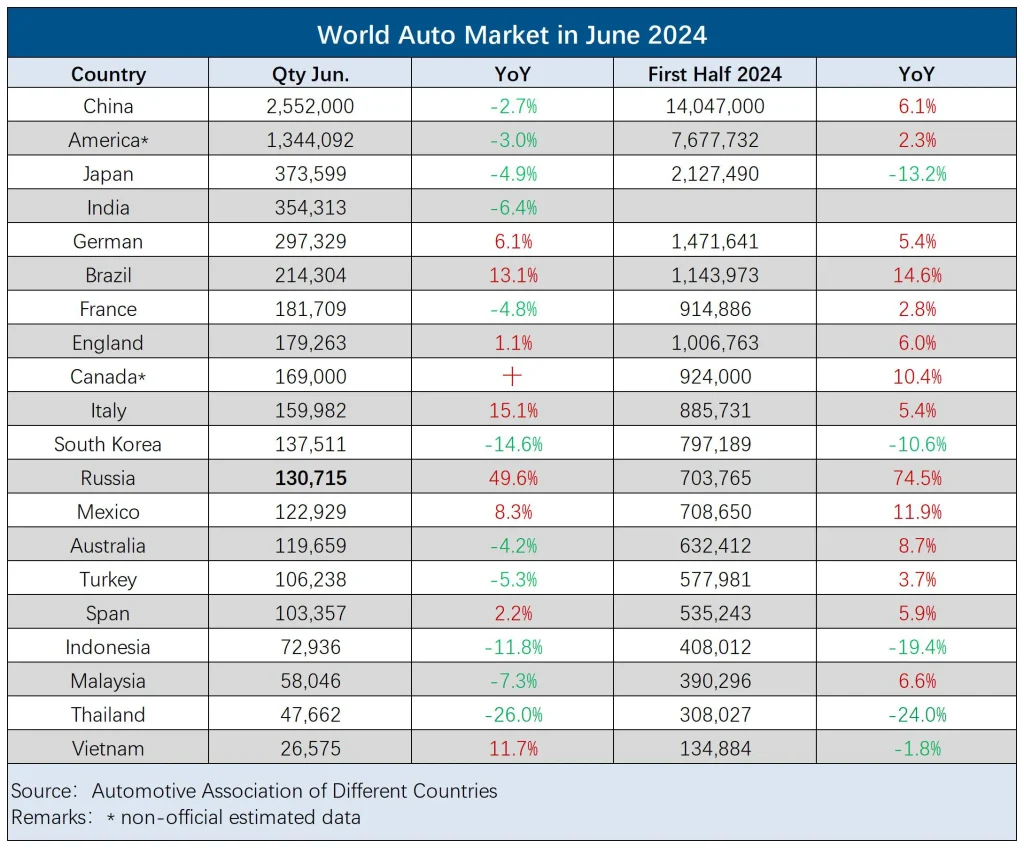
Specifically, in June, China produced and sold 2.507 million and 2.552 million vehicles, respectively, down 2.1% and 2.7% year-on-year, but up 5.7% and 5.6% month-on-month. In the first half of the year, China produced and sold 13.891 million and 14.047 million vehicles, respectively, up 4.9% and 6.1% year-on-year.
Chen Shihua, Deputy Secretary-General of the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM), noted that the ongoing old-for-new car replacement programs, the rollout of local supportive policies, the continuous launch of new models, and the mid-year sales push by car companies contributed to the month-on-month growth in June. However, he pointed out that, given the high base from the first quarter of the previous year, the growth rate in the second quarter slowed compared to the first.
Chen also mentioned that despite these factors, the automotive industry still faces significant pressures, including weak consumer confidence, intensified market competition, and increased operational pressures on enterprises. Looking ahead to the second half of the year, the continued implementation of favorable policies, such as old-for-new programs and promoting new energy vehicles (NEVs) in rural areas, along with the gradual introduction of new products, is expected to further unlock the consumption potential of China’s automotive market and support steady industry development.
Meanwhile, in the United States, challenges such as the network attack on software company CDK impacting auto dealership operations led to a decline in new car sales during the peak season. June’s new car sales were estimated at around 1.34 million units, a slight 3% year-on-year drop. According to preliminary reports from Cox Automotive and GlobalData, the seasonally adjusted annual sales rate for June in the U.S. was 15.3 million units, significantly lower than the 16.08 million units in May and 16.22 million units in June of the previous year.
Cox Automotive’s Chief Economist Jonathan Smoke stated, “The U.S. fleet market is clearly slowing, and the retail market lacks urgency. Many potential buyers are cautious, remaining ‘on the sidelines.’ However, given the expectation of lower loan rates, increased uncertainty around the national election, and continued downward pressure on new car prices, it is not surprising that buyers are hesitant.”
Despite the decline in China’s and the U.S. automotive markets, the European market rebounded with a 3.6% year-on-year increase in new car registrations in June, reversing the previous month’s decline. Driven by key markets such as Italy, Germany, and Spain, Europe’s new car registrations reached 1.31 million units. Among the five major markets, Italy (+15.1%), Germany (+6.1%), Spain (+2.2%), and the UK (+1.1%) all saw varying degrees of growth, while France experienced a 4.8% decline, mainly due to fewer working days and the impact of the elections.
Currently, high borrowing costs and sluggish economic growth across Europe are dampening overall market consumer sentiment. In the first half of the year, European car sales remained below pre-pandemic levels, with EU car sales about 18% lower than in 2019. However, the European automotive market is expected to continue its growth trend this year. Related agencies have forecast that new car registrations in the EU will reach 10.7 million units in 2024, a 2.5% year-on-year increase.
In contrast, the Japanese and Indian car markets showed signs of weakness. Japan’s new car sales in June reached 373,599 units, a 5% year-on-year decline. Since the end of last year, Japan’s automotive market has been in decline, dragged down by the Daihatsu scandal over falsified safety tests and subsequent production halts, leading to a 13% year-on-year decline in new car sales for the first half of the year.
However, with Daihatsu resuming full production in early May and gradually clearing backlogs, Japan’s car sales are expected to rebound in the second half of the year.
India’s car sales were constrained by high temperatures, with June sales down 6.4% year-on-year, including a 6.8% drop in passenger car sales to 281,566 units, the lowest since September 2022.
The Federation of Automobile Dealers Associations (FADA) of India noted that the extreme heat reduced foot traffic in dealerships by 15%, further discouraging purchases. FADA President Manish Raj Singhania stated that local dealers are facing challenges such as low customer inquiries and delayed purchasing decisions.
Despite these challenges, there is strong confidence in the long-term growth of India’s automotive market, driven by the country’s economic rise and expanding middle class. Suzuki Motor Corporation’s Executive Vice President Kenichi Ayukawa predicted that India’s car sales could reach 20 million units by 2047, buoyed by the growing prospects for electric vehicles.
Overall, while major markets like China, the U.S., India, and Japan saw declines in new car sales in June, some markets still achieved growth in cumulative sales for the first half of the year, indicating resilience in certain regions. As a result, related agencies forecast that global light vehicle sales will exceed 90 million units in 2024 and 2025, with a growth rate of 2% to 3%.
However, the agency notes that the main drivers of growth in the global light vehicle market will be Southeast Asia and India, with the U.S. and Europe likely to lag behind. Meanwhile, China’s long-term potential remains significant. Slower growth in electric vehicle (EV) sales may support short-term profits for traditional automakers but poses a challenge for the global transition to electrification.
New Energy Vehicle Market: China’s Sales Surge by 30%, Italy Soars by 40%
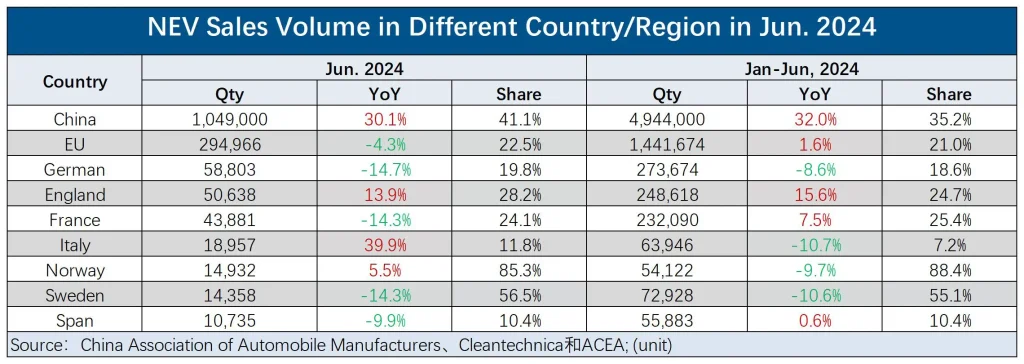
According to data from market research firm Rho Motion, global electric vehicle (including battery electric vehicles and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles) sales in June are estimated to have grown by 13% year-on-year, reaching 1.4 million units. China continued to see significant year-on-year growth, offsetting declines in European EV sales. Sales in the U.S. and Canada increased by 6% year-on-year, reaching 140,000 units.
In detail, in June, China produced and sold 1.003 million and 1.049 million new energy vehicles (NEVs), respectively, up 28.1% and 30.1% year-on-year, and 6.7% and 9.8% month-on-month. The market share for NEVs reached 41.1%, with the NEV passenger car market share at 45%.
In the first half of the year, China produced and sold 4.929 million and 4.944 million NEVs, respectively, up 30.1% and 32% year-on-year, with a market share of 35.2%. Chen Shihua highlighted that, since the association started keeping statistics over a decade ago, the cumulative production and sales of domestically produced NEVs exceeded 30 million units as of the end of June this year.
Wu Songquan, a senior chief expert at the China Automotive Technology & Research Center, stated that the rapid growth in NEV production, sales, and ownership indicates improving vehicle quality, gaining recognition and acceptance from more users.
Wu also noted that, looking ahead to the second half of the year, the launch of many new models, vehicle value enhancement, in-depth implementation of old-for-new policies, and the country’s strong support for developing new quality production capacity will contribute to further growth in China’s NEV market. Overall, China’s NEV production and sales are expected to reach 11.5 million units this year.
While China’s NEV market maintained rapid growth, Europe’s automotive market faced significant pressure from the transition to electrification. In June, EV sales (including battery electric vehicles and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles) in Europe fell by 4.3% year-on-year to 290,000 units, with a market share of 22.5%.
In Europe, pure electric vehicle sales slightly increased by 0.1% year-on-year, but the market share fell from 16.5% a year ago to 15.9%, mainly due to growth in Belgium and Italy failing to offset double-digit declines in Germany, the Netherlands, and France.
Reflecting on the first half of the year, Europe’s EV sales reached 1.44 million units, up 1.6% year-on-year, with a market share of 21%. Pure electric vehicle sales in Europe reached 950,000 units, a slight increase of 1.6% year-on-year, but the market share dropped from 14.2% in the same period last year to 13.9%, contrary to the industry’s expectations for accelerated market transformation towards EVs.
Specifically, in June, EV sales in Germany, France, Spain, and Sweden declined.
In Germany, the largest EV market in Europe, EV sales dropped nearly 15% in June, with a market share of less than 20%. In the first half of the year, EV sales in Germany fell by 8.6%, with a market share decline to 21.2%. This decline is mainly due to the government’s reduced incentives for EV purchases.
Germany’s Federal Motor Transport Authority (KBA) data showed that in June, pure electric vehicle registrations in Germany fell by 11% year-on-year, a decline for the fourth consecutive month. In the first half of the year, pure electric vehicle registrations declined by nearly 2% year-on-year.
In addition to the incentive policy shift, Germany’s EV market is also facing challenges such as insufficient charging infrastructure and relatively high energy prices. BMW CEO Oliver Zipse said that Germany needs a comprehensive policy to encourage the electrification transition, pointing out that the main problem with EVs is infrastructure, particularly in densely populated areas.
However, in June, the electric vehicle (EV) sales in two other major European automotive markets, the United Kingdom and Italy, grew by nearly 14% and 40%, respectively, primarily due to local government policies.
In the UK, driven by zero-emission vehicle policies, EV sales in June reached 50,000 units, with market share increasing from 25.1% in the same period last year to 28.2%. Specifically, sales of pure electric vehicles (EVs) in the UK saw a slight year-on-year increase of 7.4%, while sales of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) surged by 30%.
The Italian EV market benefited from the government’s long-awaited subsidies, leading to more than a doubling of pure EV deliveries in June. However, as consumers waited for government subsidies, they delayed their purchasing decisions in previous months, causing Italy’s EV sales in the first half of the year to decline by more than one-fifth.
Industry analysts pointed out that due to the high cost of EVs and economic downturns affecting consumers’ willingness to buy big-ticket items, the European EV market remains sensitive to subsidies and policies.
Renault brand CEO Fabrice Cambolive recently mentioned at a conference, “This is a market extremely sensitive to policy changes; new incentives have stimulated demand for EVs, while the demand for plug-in hybrids is actually driven by customers.”
Overall, factors such as range anxiety, uncertain economic outlook, and the lack of affordable models limit the further adoption of EVs, putting considerable pressure on the global EV market.
According to related agencies, global EV sales exceeded 14 million units in 2023, with market share rising from 2.5% in 2019 and 13% in 2022 to 16.5%. In the first half of 2024, China’s EV sales growth remained strong, while the US and Europe saw moderate growth, though slower compared to the peaks of 2020-2021.
The agency believes that the pricing dynamics of EVs, the dilution effect of EVs on the profits of most traditional OEMs, and changes in government subsidies could affect EV sales, potentially causing the EV market share in the US and Europe to remain stable or decline. In contrast, in the Chinese market, price reductions and a wide range of models will continue to put pressure on traditional gasoline vehicles and drive the adoption of EVs.
