
Selecting the appropriate electric vehicle (EV) charger involves various factors, with amperage being one of the most critical. The amperage of a charger determines how quickly your vehicle can recharge and whether your home electrical system can accommodate it.
If you’re new to EV charger installation, start with our complete overview: The Ultimate Guide to EV Charger Installation at Home.
In this guide, we’ll explore the differences between 16Amp, 32Amp, 40Amp, and higher amperage options to help you make an informed decision.
1. Understanding Amperage and Charging Speed
Electric vehicle (EV) charging is influenced by both voltage and amperage. These factors combine to affect the charging speed, cost, and overall user experience. We will examine EV chargers ranging from 16A to 80A and see how these relate to Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 charging standards.
2. Overview of Charging Levels
- Level 1: Utilizes a standard 120V household outlet, typically delivering 1.4kW to 1.9kW for slow charging. This level is suitable for daily commuting and plug-in hybrid vehicles.
- Level 2: Employs a 240V outlet, providing between 3.3kW and 19.2kW, which significantly accelerates the charging process. It’s ideal for home, public, and long-distance driving use.
- Level 3 (DC Fast Charging): Supplies 50kW to 350kW of direct current (DC), mainly at public charging stations for rapid top-ups.
3. Amperage Variability in Level 1 and Level 2 Charging
Different amperage ratings impact charging performance under Level 1 and Level 2 scenarios as follows:
3.1 Level 1 Charging:
- 16A: Provides a maximum output of 1.9kW, adding about 3-5 miles of range per hour, ideal for smaller battery vehicles or those without rapid charging needs.
3.2 Level 2 Charging:
- 16A: Offers up to 3.8kW, enhancing range by approximately 8-12 miles per hour, suitable for most daily requirements.
- 32A: Delivers 7.7kW, increasing range by about 17-25 miles per hour, greatly reducing charging time and is a popular choice for residential setups.
- 40A: Provides 9.6kW, enhancing range by about 20-30 miles per hour, perfect for those with higher driving demands.
- 48A: Supplies up to 11.5kW, increasing range by about 25-38 miles per hour, frequently chosen for fast charging at home and commercial environments.
- 80A: Yields up to 19.2kW, with range gains of about 40-50 miles per hour, typically used for commercial rapid charging and high-performance EVs.
4. Charging Speed Comparison Across Amps and Levels
Considering an 85 kWh battery, let’s explore the charging speeds at various amperages and levels, taking into account different vehicle trims and power consumption. The table below illustrates how amperage and charging level interact to influence charging performance.
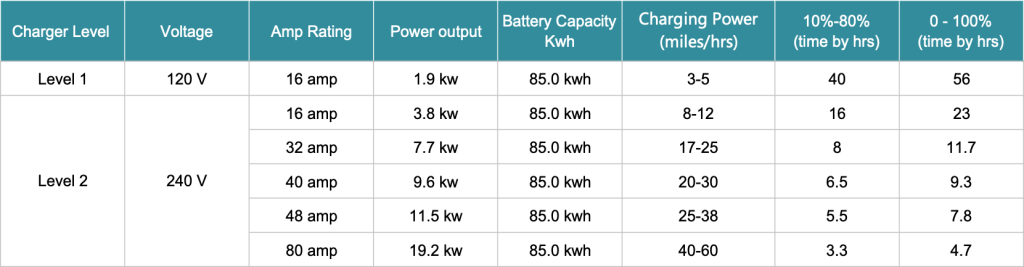
5. Installation and Cost Implications for Higher Amp Chargers
16A Chargers
Chargers with a 16A rating are typically the simplest and most cost-effective to install. They can often use existing 120V or 240V outlets, which means they do not usually require additional electrical work. This makes them an ideal choice for EV owners who need minimal additional charging capacity.
32A and 48A Chargers
For chargers within the 32A to 48A range, installation can become more complex and potentially more costly, particularly if it involves upgrading your home’s electrical panel—a significant expense. However, there are cost-effective strategies to consider if your current panel capacity can handle the additional load of an EV charger:
- Circuit Sharing: One way to reduce costs is to share the charger’s circuit with other appliances, such as a clothes dryer. This setup would require a double throw double pole (DTDP) switch, allowing you to charge your vehicle overnight and use the dryer during the day.
- Adding a Circuit with Dynamic Load Management: Another approach is to add a new circuit with a dedicated breaker and integrate a Dynamic Circuit Capacity Controller (DCC). This system monitors the overall electrical load of your home and adjusts the charger’s power output accordingly to prevent overloading.
It’s essential to consult with a professional electrician to determine which of these options is suitable for your specific situation. For more detailed guidance, refer to our upcoming article on how to install an EV charger at home.
80A Chargers
Installing an 80A charger often requires significant upgrades to your home’s electrical infrastructure, including a major panel upgrade or even a new service installation from your utility provider. This level of upgrade is more common in commercial settings or for EV owners with high-performance vehicles and demanding charging needs.
Given the high costs associated with such installations, it’s crucial to assess whether the benefits justify the investment, based on your vehicle’s charging requirements and your frequent usage patterns.
6. Choosing the Right Amperage and Charging Level for Your EV
When deciding on the best amperage for your electric vehicle (EV) charger, it’s essential to consider factors such as your vehicle’s specifications, your typical driving habits, and the overall cost implications of different setups.
6.1 Vehicle Specifications
Different EV models have varying onboard charger (OBC) capacities, which can limit the maximum effective amperage of your home charging setup.
For example, a Subaru Solterra, which has an OBC capacity of only 6.6 kW, won’t benefit from a charger that delivers more than this, even if the charger’s capacity is higher.
On the other hand, vehicles like Hyundai or Kia models support up to 11.5 kW, making them compatible with higher amperage chargers for faster charging speeds.
6.2 Driving Habits
Your charging needs largely depend on how much you drive daily. For those with short commutes, averaging around 40 miles, a basic Level 1 charger or a 16A Level 2 charger is usually sufficient.
However, for longer commutes or frequent long-distance travel, a higher amperage charger, such as 32A or above, may be necessary to ensure your vehicle is always ready to go.
6.3 Cost Considerations
The cost of installing a higher amperage charger can vary significantly. A 16A charger typically does not require special installation beyond a standard outlet, which can be a cost-effective option.
Moving up to a 32A or 40A charger might necessitate additional electrical work, like upgrading your home’s electrical panel or installing a dedicated circuit.
Chargers with 80A capacity often involve significant electrical infrastructure upgrades, which can be prohibitively expensive unless truly necessary based on your vehicle’s compatibility and charging needs.
Conclusion
Selecting the ideal amperage for an EV charger is a crucial decision that impacts not only the charging efficiency but also the overall user experience and integration with existing home electrical systems.
By understanding the different amperage options and how they correspond to vehicle specifications, driving habits, and cost considerations, EV owners can make informed choices that optimize their charging setups. It’s essential to balance the desired charging speed with practical aspects such as installation costs and electrical capacity.
Whether opting for a modest 16A charger for daily commuting needs or a more robust 80A setup for high-demand scenarios, the right charger can significantly enhance the convenience and efficiency of owning an electric vehicle.
With careful planning and consideration, you can select a charging solution that meets your needs today and remains adaptable for future advancements in EV technology.
