
As electric vehicles (EVs) gain popularity worldwide, understanding the different EV charger standards has become crucial for consumers and manufacturers alike. Charging standards vary by region and influence not only how EV owners charge their vehicles but also impact cross-border travel, vehicle sales, and infrastructure development. In this guide, we will explore the major global EV charging standards, their technical background, and the future trends shaping the EV industry.
Why EV Charger Standards Matter
EV charging standards are more than just technical requirements. They determine the compatibility between charging stations and vehicles and influence the ease of cross-border EV travel. In Europe, unified standards allow drivers to seamlessly travel across multiple countries, while in North America and parts of Asia, the diversity of standards can complicate cross-national journeys.
Industry impact is another significant factor. Automakers and charging station operators must adjust their products and services based on the market’s standards. For example, Tesla adapts its charging systems across different regions. In North America, Tesla uses its proprietary Tesla NACS standard for its Supercharger network. However, in Europe, Tesla vehicles adopt the local Type 2 (AC charging) and CCS2 (DC fast charging) standards. This ensures compatibility with Europe’s charging infrastructure, where Type 2 and CCS2 are mandatory for all EVs. In China, Tesla vehicles use the GB/T standard to comply with the country’s charging regulations, meaning Tesla vehicles there are equipped with local charging ports.

Additionally, in North America, Tesla has gradually increased support for CCS1 in two ways: first, by offering a CCS to Tesla adapter that allows Tesla vehicles with NACS ports to charge at public CCS stations, and second, by adding Tesla to CCS Adapter directly at some Supercharger stations. This enables non-Tesla vehicles to access Tesla’s fast-charging network, expanding its utility.
The Major Global EV Charging Standards
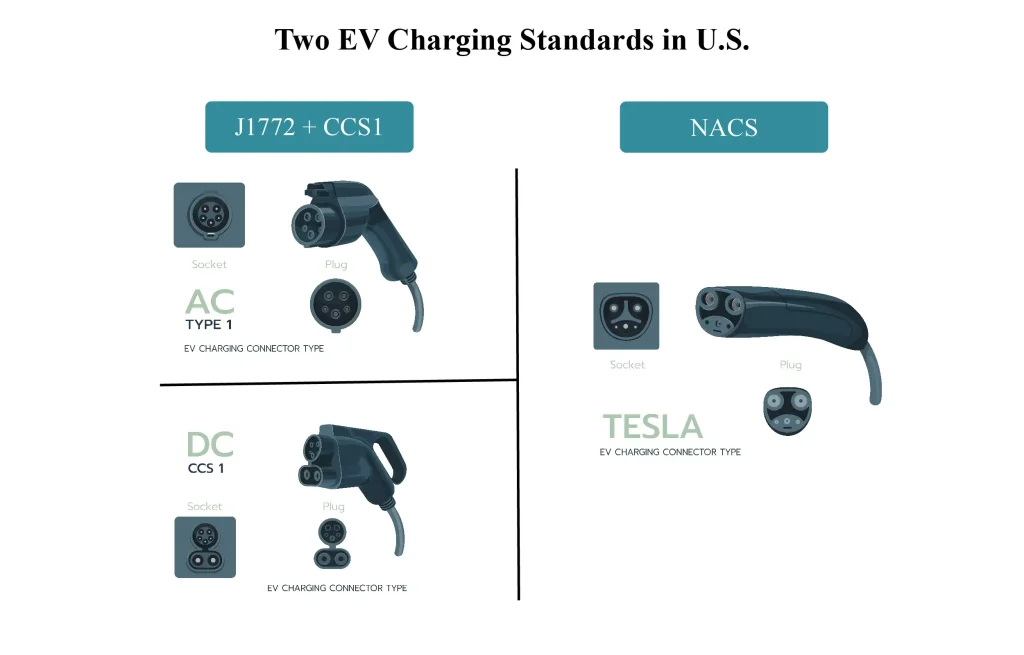
1. CCS (Combined Charging System)
- Technical Details: CCS integrates both AC and DC charging, offering dual-mode charging through the same connector. It allows vehicles to charge using slow AC at home or use fast DC at charging stations.
- Regional Differences: CCS1 is primarily used in North America, while CCS2 dominates in Europe. Though the physical connectors differ, the underlying technology is the same. Recently, North American automakers like Rivian and Lucid Motors have begun adopting CCS2 connectors, recognizing the global advantages of aligning with this widely used standard.
- Future Trends: CCS is expected to continue expanding globally, especially in Asia, where it may become the dominant charging standard in the coming years.
2. Type 1 (SAE J1772)
- Development History: Also known as SAE J1772, Type 1 is a single-phase AC charging standard developed by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), primarily used in North America and Japan.
- AC Charging Capacity: Power Calculation (Common Installations): Type 1 is commonly used in 240V single-phase systems. The most typical configurations include: 32A Circuit: Provides up to 7.7kW (calculated as 240V x 32A = 7.7kW). 40A Circuit: Offers a maximum of 9.6kW (calculated as 240V x 40A = 9.6kW). Higher Power Options: 48A Circuit: In more advanced home or commercial setups, Type 1 can support up to 11.5kW (calculated as 240V x 48A = 11.5kW). 80A Circuit: For high-end installations, the maximum supported power can reach 19.2kW (calculated as 240V x 80A = 19.2kW). This is commonly used in commercial or specialized high-power home charging stations.
- Charging Speed: Depending on the configuration: 32A: Adds approximately 25-30 miles of range per hour. 48A: Adds approximately 35-40 miles of range per hour. 80A: Adds up to 60 miles of range per hour, making it one of the fastest home AC charging options.
- Limitations: Type 1 offers slower AC charging compared to three-phase AC charging systems like Type 2. Although CCS1 supports both AC and DC charging, SAE J1772 remains widely adopted in North America due to its early market penetration and the existing infrastructure.
3. Type 2 (IEC 62196-2)
- Advantages of Three-Phase AC Charging: Type 2 is the standard across Europe, supporting both AC and DC charging. It offers three-phase AC power, allowing for faster charging at public stations.
- AC Charging Capacity: Single-Phase Power Calculation: In single-phase installations, Type 2 operates at 230V with 32A, offering up to 7.4kW (calculated as 230V x 32A = 7.4kW), similar to Type 1. Three-Phase Power Calculation: In three-phase setups, Type 2 can provide significantly higher power, up to 22kW (calculated as 400V x 32A x √3 = 22kW). This is common for public charging stations in Europe, providing faster charging than single-phase systems. Charging Speed: For three-phase systems, the charging rate can reach approximately 75-80 miles of range per hour, which is much faster compared to single-phase charging.
- DC Support: Type 2 is integrated with CCS2, enabling the same connector to handle both AC and DC charging. While Type 2 is used for regular AC charging, CCS2 adds extra DC terminals for fast charging when needed.
4. CHAdeMO
- Japan’s Technical Evolution: CHAdeMO is a Japanese-developed DC fast charging standard initially designed to meet the needs of domestic automakers like Nissan and Mitsubishi. However, as these manufacturers have lagged in the global EV race, CHAdeMO’s influence is diminishing internationally.
- Global Expansion: While CHAdeMO remains dominant in Japan, it faces stiff competition from CCS in other markets. Its global presence has been reduced, especially in Europe and North America.
5. GB/T
- China’s Unique Market: GB/T is China’s national EV charging standard, supporting both AC and DC charging. As Chinese automakers like BYD and NIO grow their global footprint, GB/T’s influence is expanding internationally, particularly in emerging markets where Chinese EV exports are increasing.
6. Tesla NACS
- Tesla’s Influence: Tesla developed the NACS standard, which has dominated the North American market. It supports both AC and DC charging, and Tesla’s extensive Supercharger network has cemented its position. Recently, automakers like Ford and GM have announced plans to support Tesla NACS in their future models, further solidifying its place in the market.
- Future Plans: With more automakers adopting NACS and Tesla opening its Supercharger network to non-Tesla vehicles, NACS could become the dominant standard in North America.
Charging Standards by Region
1. North America
- Policy Impact: North America’s charging landscape is dominated by CCS1 and Tesla NACS. With major automakers like Ford and GM planning to support NACS, the competition between charging standards is intensifying.
2. Europe
- Type 2 and CCS2: Europe’s use of unified Type 2 and CCS2 standards ensures widespread compatibility for EVs. This standardization makes cross-border EV travel within Europe easier and more convenient.
3. Asia (China, Japan, South Korea)
- China’s GB/T: As China’s EV export market grows, GB/T is gaining international influence, especially in emerging markets.
- Japan’s CHAdeMO: Despite its dominance in Japan, CHAdeMO is losing ground globally as other standards, particularly CCS, gain traction in the international market.
The diversity of global EV charging standards reflects the unique technological and policy needs of different regions. Understanding these standards helps EV owners choose the right charging solutions while also assisting automakers and policymakers in navigating future technological and market changes. Staying informed about global charging standards is essential for preparing for the future of electric mobility.
